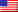
For decades, the Concorde represented the pinnacle of air travel—a luxury enjoyed by the elite, but ultimately unsustainable. Retired in 2003, the supersonic jet left behind a legacy of engineering marvel and economic impracticality. Now, with new technologies and a renewed focus on speed, the question isn’t if supersonic flight will return, but how.
The Concorde’s Engineering Legacy
The Concorde wasn’t just fast; it was an unprecedented feat of engineering. Its delta wings, high-bypass turbofan engines, and heat-resistant materials allowed it to cruise at Mach 2 (twice the speed of sound), slashing transatlantic flight times. However, this came at a cost: high fuel consumption, sonic booms over populated areas, and limited passenger capacity. Former Chief Engineer John Britton recalls the challenges of maintaining such a complex machine, highlighting the precision required for every flight.
Overcoming the Challenges
Today’s attempts to revive supersonic travel face similar hurdles, but with potential solutions. Dr. Kshitij Sabnis of Queen Mary University of London explains that reducing sonic booms is key. New aircraft designs, like “quiet supersonic technology,” aim to shape shockwaves to minimize ground noise. Another issue is efficiency: Concorde burned massive amounts of fuel. Modern designs, including those being developed by Boom Supersonic, seek to improve fuel efficiency through lighter materials and optimized aerodynamics.
Boom Supersonic: Making Supersonic Travel Accessible?
Blake Scholl, CEO of Boom Supersonic, envisions a future where supersonic flight isn’t exclusive to the wealthy. His company’s Overture jet aims to fly at Mach 2.2 over water, reducing the impact of sonic booms on land. Scholl believes that lowering costs through innovative manufacturing and efficient engines will make supersonic travel viable for a broader market. However, significant financial and logistical hurdles remain, including regulatory approvals and the development of sustainable aviation fuels.
Supersonic flight is poised for a comeback, driven by technological advancements and a persistent desire for faster travel. While the Concorde’s era was defined by exclusivity, the next generation of supersonic jets promises to address the issues of cost, environmental impact, and accessibility, potentially reshaping the future of long-distance air travel.